Cell Marque Mucins Antibody Panel
Products are for professional/laboratory use only.
Modern understanding of gastrointestinal barrier is associated with the ability of surface and glandular epithelial cells to synthesize mucin. Epithelial mucins are a large group of secreted and embedded in plasmolemma glycoproteins produced by epithelial cells.
In epithelial tissues 13 types of mucin are distinguished, forming two classes of compounds: transmembrane and secretory mucins.
MUC1 is one of the transmembrane mucins of the digestive tract cells. MUC3 and MUC4 are membrane-bound mucins that play important roles in the protection of the epithelial cells and have been implicated in epithelial renewal and differentiation. As for the gel-forming mucins of the digestive tract, they include: MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6. They are actively expressed on epithelial cells and the expression of membrane glycoproteins increases nearly tenfold in transformed cells.
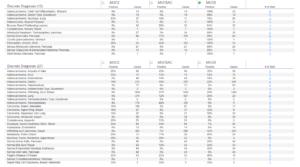
MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6 are sometimes used together in panels to distinguish neoplasms in the GI tract and below are some examples of combinations where these antibodies are used in diagnosis. On the other hand, MUC4 is primarily used by labs to diagnose low grade fibromyxoid sarcomas.
Technical references:
- Lee, H. K., Kwon, M. J., Seo, J., Kim, J. W., Hong, M., Park, H. R., Min, S. K., Choe, J. Y., Ra, Y. J., Jang, S. H., Hwang, Y. I., Kim, H. Y., & Min, K. W. (2019). Expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) in ALK-positive lung cancer: Comparison with EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Pathology, research and practice, 215(3), 459–465 – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30580903/
- Lee, M., Lee, H., Kim, W. et al. Expression of Mucins and Cytokeratins in Primary Carcinomas of the Digestive System. Mod Pathol 16, 403–410 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1097/01.MP.0000067683.84284.66
- Doyle, L. A., Möller, E., Dal Cin, P., Fletcher, C. D., Mertens, F., & Hornick, J. L. (2011). MUC4 is a highly sensitive and specific marker for low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. The American journal of surgical pathology, 35(5), 733–741. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e318210c268