ZytoVision Unique* in FISH and CISH – ZytoLight SPEC USP6 Dual Color Break Apart Probe
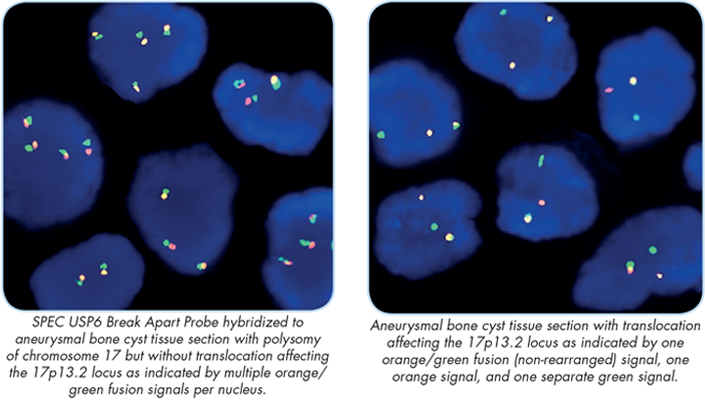
Products are for professional/laboratory use only. The ZytoLight SPEC USP6 Dual Color Break Apart Probe is designed to detect translocations involving the chromosomal region 17p 13.2 harboring the USP6 gene. Translocations affecting USP6 have been initially found in primary aneurysmal bone cysts (ABC), a benign but locally aggressive bone lesion that occurs predominately during the first two decades of life. USP6 rearrangements are restricted to spindle cells in primary ABC, indistinguishable from surrounding normal spindle cells. The resulting fusion genes detected are formed by juxtaposition of the USP6 coding sequences to the highly active promoter sequences of several partner genes, as e.g. CDH11, COL1A1, OMD, TRAP150, and ZNF9, leading to the transcriptional upregulation of USP6. No true fusion genes are formed.
More recently, nodular fasciitis (NF), another mesenchymal lesion, has been tested positive for USP6 rearrangements. NF is a subcutaneous pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic profliferation of unknown pathogenesis that regresses spontaneously when not surgically resected. The translocation results in the fusion of the promoter region of MYH9 located on 22q12.3 to the entire coding sequence of USP6 and subsequently in upregulated USP6 expression. For both lesions, it is assumed that the detection of USP6 rearrangements by FISH might represent a valuable diagnostic tool.
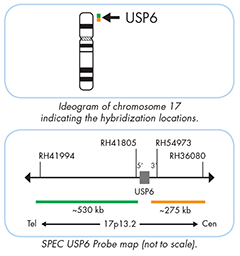
The SPEC USP6 Dual Color Break Apart Probe is a mixture of two direct labelled probes hybridising to the 17p13.2 band. The orange fluorochrome direct labelled probe hybridises proximal to the USP6 gene and the green fluorochrome direct labelled probe hybridises distal to that gene.
Ordering Information:
|
Product Code |
Description |
Tests (Volume) |
|
ZYZ215150 |
ZytoLight SPEC USP6 Dual Color Break Apart Probe |
5 (50µl) |
*Based on publicly available data. Only CE IVD products were considered for the comparative analysis. Please check regulatory status in your country.
References:
Erickson-Johnson MR, et al. (2011) Lab Invest 91: 1427-33.
Nakamura T, et al. (1988) Oncogene Res 2: 357-70.
Oliveira AM, et al. (2004) Cancer Res 64: 1920-3.
Oliveira AM, et al. (2005) Oncogene 24: 3419-26.